The Drug Approval Process In Japan

The drug approval process in Japan is less complex and easy when compared to some other countries beyond the language barriers. In addition to regulatory considerations, the PMDA offers sponsors consultation to assist them in understanding the prerequisites and the detailed procedure for drug approval. As a result of this positive change, many manufacturers choose to register and sell their medicines in Japan.
Note: This article was revised & updated in August 2022.

Japan’s pharmaceutical market is one of the largest markets in the world. The Japanese pharmaceutical market will expand at a CAGR of 1.06% from 2022 to 2027 as per a report. Japan’s gross domestic product (GDP) is around $5 trillion. The market value, which includes non-prescription medications, is about $95 billion from the figures of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW).
Various analysis reports also prove that the country’s market for drugs and medical devices will continue to grow further. According to experts, this occurs due to the rapidly aging population and the need for new medications to treat related conditions. Japan imports about 35% of its prescription medications from the US, and this demand is growing day by day.
Regulatory authority for drug approval in Japan
There are the two crucial regulatory bodies that review and approve drugs and medical devices in Japan are
- Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), and
- Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW).
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) services
PMDA provides the following services in drug regulatory
- Consultation
- Pharmaceutical affairs consultation on R&D strategy
- Clinical trial consultation
- Pre-market review
- Re-examination
- Re-evaluation
- Use-results evaluation
- Safety measures
- Relief services for adverse health events
According to the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law, sponsors should submit all forms related to the marketing application in Japanese.
Who can apply for drug approval?
A qualified local entity who has a Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH) or a Designated Marketing Authorization Holder (DMAH) can register, import, and sell medical products in the Japanese market.
How can a foreign manufacturer market drugs in Japan?
To gain market approval for drugs and medical devices, foreign manufacturers need to fulfill the following criteria:
Foreign Manufacturer Accreditation (FMA)
- A foreign manufacturer is an individual overseas company that intends to manufacture drugs, quasi-drugs, cosmetics, or medical devices and import them into Japan.
- Foreign manufacturers need to obtain a Foreign Manufacturer Accreditation (FMA) from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare to market their products in Japan.
Foreign Restrictive Approval
- For the foreign pharmaceutical manufacturers, It is possible to apply for market approval directly under their name.
- Along with other necessary procedures, foreign manufacturers need to perform clinical studies to demonstrate the quality, efficacy, and safety of the drugs they intend to export to Japan.
Fee for New Accreditation for foreign manufacturers
The fee for New Accreditation
- MHLW fee 90,000 JPY
- PMDA fee 143900 JPY
Need support for your drug registration in Japan?
Credevo offers expertise in drug product registration, clinical trial regulations, and many more services in Japan. Check them out now!
The Investigational New Drug (IND) approval process in Japan
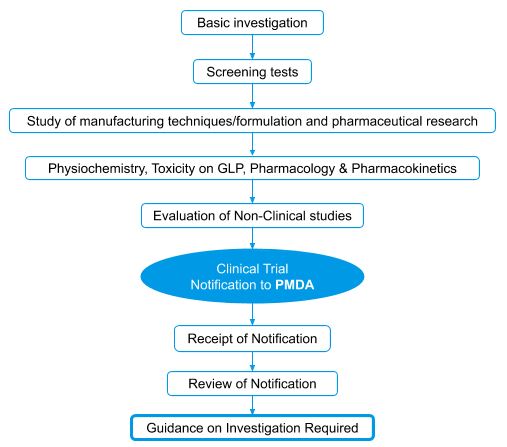
- The Japanese regulatory authority follows the Common Technical Document (CTD) drug application format and hence the applicant should prepare the Investigational New Drug (IND) application and documents as per the CTD format.
- Before making an application, the applicant may schedule a pre-IND consultation with PMDA as such consultations help to ensure a flawless and streamlined IND application process.
- Initial IND consultations may take up to 30 days, but subsequent consultations may only require 14 days.
- After the applicant applies, the PMDA evaluates the preclinical data, protocols for clinical studies, and other necessary documents.
- During the evaluation, the applicant must respond promptly to the PMDA’s questions..
- Once the PMDA completes its review, then the next step is to get approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB). The IRB takes about 1- 4 weeks for review and approval.
- The sponsor can begin clinical trials on human subjects if the IRB approves the IND application following a favorable response.
Investigational New Drug (IND) approval process flow
New Drug Application (NDA) approval process in Japan
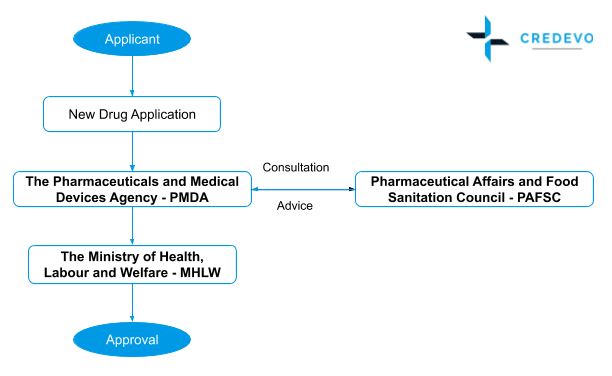
- Applicant submits the New Drug Application (NDA) forms to the PMDA for market approval.
- The PMDA then reviews the application, and if they feel necessary, may schedule a face-to-face meeting with the applicant.
- During the meeting, the applicant needs to discuss and answer the queries from PMDA, and after the face-to-face meeting, the PMDA reviewer prepares a review report.
- If the PMDA finds any critical issues during the review, it organizes an Expert Discussion. It involves a discussion between the PMDA reviewer and external expert on the proposed critical issue.
- After review, the experts submit the results along with GMP conformity investigation reports to the Ministry of Health and Labor Welfare (MHLW).
- The MHLW, upon consultation with the Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC), the Ministry of Health and Labor Welfare (MHLW) may approve the New Drug Application (NDA).
- After the approval, the MHLW’s Evaluation and Licensing Division issues the approval certificate.
- The PMDA delivers the approval certification for the drugs reviewed by the bureau.
Regulatory process flow for New Drug Application (NDA) approval
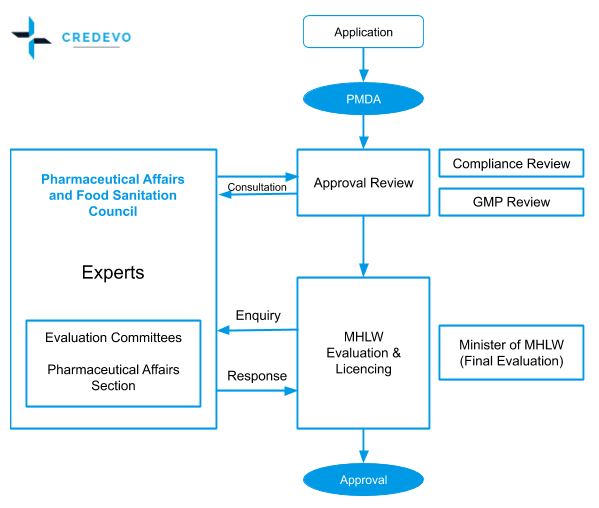
Complete overview of the approval process in Japan
Orphan drug regulatory in Japan
Japan defines a disease as rare if fewer than 50,000 people are affected. Pharmaceutical companies can request orphan drug designation to treat such rare diseases.
Criteria for drugs to obtain orphan drug designation
- The medical need is very high.
- The intended use is for severe diseases such as intractable diseases.
- In addition, the drug needs to meet the following conditions
- No other drug or medical treatment is available for the disease.
- The product under review exhibits significantly high efficacy and safety compared with existing products.
The generic drug approval process in Japan
In Japan, the PMDA reviews generic drug applications, and this includes the assessment of bioequivalence studies. This bioequivalence assessment helps to confirm the quality, efficacy, and safety of the product based on documents submitted by applicants.
In Japan, the drug product is considered to be a generic drug, if it covers the following criteria
- It contains an API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient),
- If the API has a different hydrate form or crystalline form from the original drug, and
- If the API has the same chemical structure as the original drug.
Biologics & biosimilar drugs regulatory in Japan
Biologic drugs
- The PMDA’s office of biologicals provides consultations concerning clinical trials of new biologic drugs and handles biotechnology medicines, which includes biosimilars.
- Requirements for biologic drugs differ from general drugs and depend on whether a biological product is a regenerative medicine product or not.
- The MHLW designates a product as a biological drug after its consultation with the Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC).
Biosimilar drugs
Biosimilar drugs are considered as those drugs that are “equivalent and homogenous to the reference biological product in terms of efficacy, quality, and safety.”
- In Japan, the approval of biosimilar products tends to reduce the amount of new information required and the timeline for approval.
- The applicant can reduce the burden in case if it has information gathered for its foreign license or approval.
The approval process for biosimilars in Japan
- Applicants who fulfill all the requirements of biosimilars can submit the market approval application to the Ministry of Health and Labor Welfare (MHLW), which will pass it further to the PMDA. At this stage, reviewers may look to visit manufacturing units.
- During this review process, reviewers assess the entire file and schedule meetings with the owner. As a result, the applicant gets a chance to discuss all aspects of the approval of this product.
- Once the review ends, the PMDA produces a detailed report and forwards it to the Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau of the MHLW.
- Upon receipt and review of this report, the MHLW grants or refuses the market approval of the biosimilar and if approved, determines the price.
The fast track approval process for drugs in Japan
The PMDA or the respective authority conducts the drug application reviews in the order of application forms received. However, in some cases, the authority reviews the applications in priority for special category drugs.
Priority review
The application shall fall under one of the following criteria to get priority review.
- Based on the seriousness of diseases
- The diseases which have important effects on a patient’s survival.
- The disease which is progressive and irreversible and has marked effects on daily life.
- Where there is no existing method of treatment, prophylaxis, or diagnosis.
- If the drug has a greater therapeutic use concerning existing treatment.
Products under priority review get priority at every stage of the approval process as much as possible.
Priority review process
- When drugs are designated for priority review, PMDA consults experts for opinions and reports them to the MHLW.
- Based on this report of PMDA, the Evaluation and Licensing Division of MHLW decides whether or not to designate the drug for priority review.
- After that, the Evaluation and Licensing Division will notify its decision to both the applicant and the PMDA.
- When the authority selects a drug for priority review during its development, it is possible to obtain priority interview advice on indications and other items concerning the product.
- As the authority handles all orphan drugs for priority interview advice, and hence a separate application is not required.
- Applicants should submit the results of clinical trials up to late Phase II to estimate the clinical usefulness.
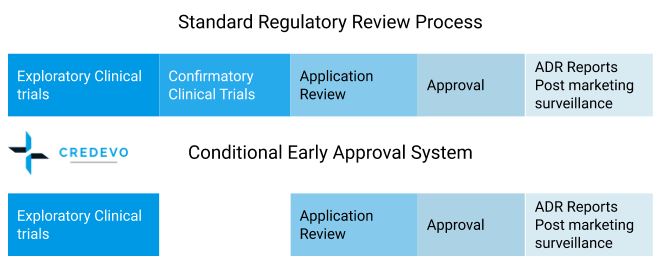
The conditional accelerated approval system
A conditional accelerated approval system is applicable for the drugs used to treat serious diseases and/or occur in a small number of patients where effective treatment is not available.
In the conditional accelerated approval system, the results of the clinical trial are not required, but the conduct of post-marketing surveys is necessary as a condition for approval by the Pharmaceutical Evaluation Division.
Criteria for the drug applications to come under the conditional accelerated approval system
- Based on the seriousness of the indication
- The disease has a significant impact on public health.
- The disease is progressive and irreversible.
- When there are no existing remedies available.
- Shows good efficacy and safety with fewer physical and mental side effects, when compared with the current treatments.
Are you planning to register & market your medicinal product in JAPAN?
Credevo offers a wide range of drug development and regulatory services in Japan. Choose one of the following options to connect with us.
Get the report on the drug registration process in Japan.
Note: This report will be charged @ $1424.
Do you have a query? Just ask experts at Credevo.
Note: “Ask Credevo Expert” will be charged @ $50 / inquiry. Any inquiry requiring more than 30 min of the expert’s time will incur additional charges.
Looking for a quotation? Just provide relevant info and we will send you the details.
References
- https://www.thepharmaletter.com/article/japan-pharma-market-review
- https://marketrealist.com/2016/04/drugs-priced-japan/
- https://www.pmda.go.jp/english/about-pmda/0004.html
- http://www.jpma.or.jp/english/parj/pdf/2018.pdf
- http://www.nifds.go.kr/brd/m_95/down.do?brd_id=board_mfds_411&seq=21651&data_tp=A&file_seq=1







