

Monetary policy refers to the policy of the government to use the interest rate and money supply to manage aggregate demand in an economy in order to achieve macroeconomic objectives. It can be an expansionary monetary policy or a contractionary monetary policy.
In this article, we will explain the expansionary monetary policy in detail along with a brief discussion of the contractionary monetary policy.
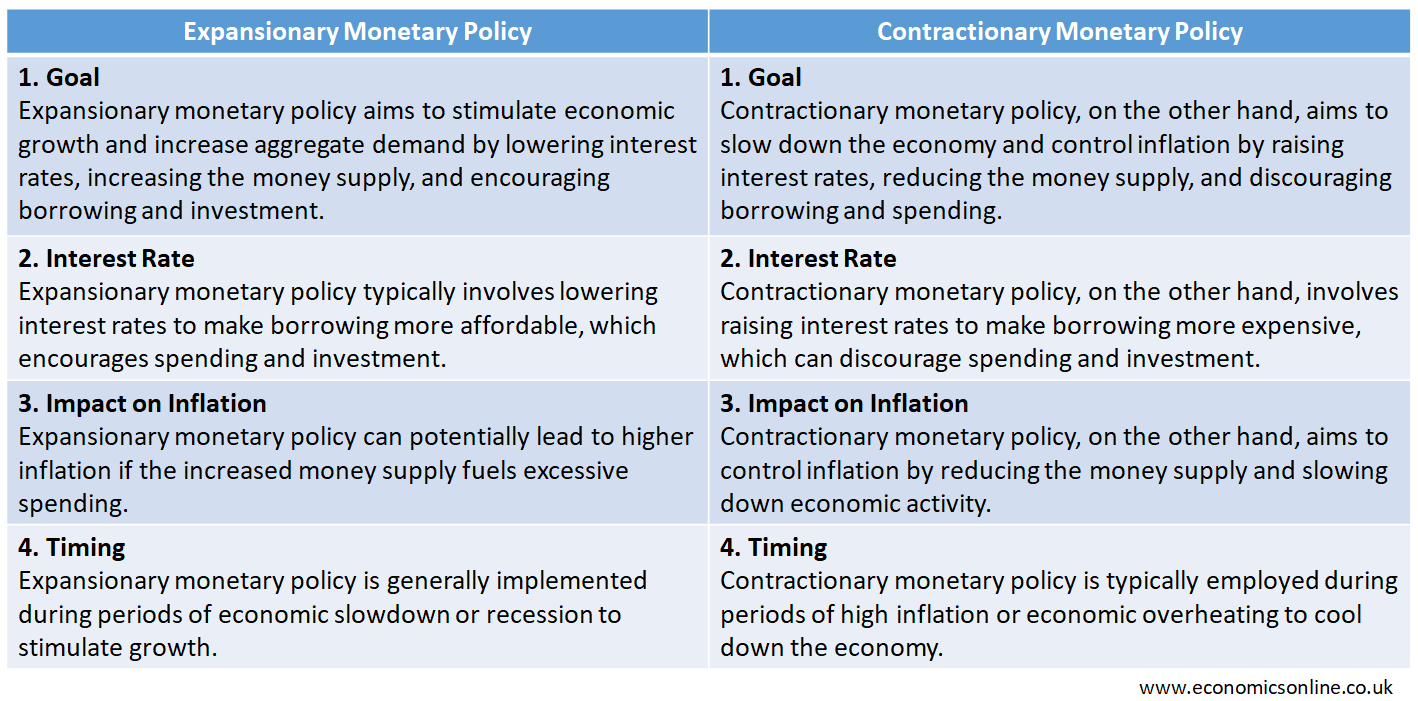
Expansionary monetary policy refers to the policy of the government to decrease the interest rate and increase the money supply in order to increase aggregate demand in an economy to increase output and employment levels.
An example of expansionary monetary policy is when a central bank such as the Federal Reserve (Fed) lowers interest rates to encourage individuals and firms to borrow and spend more, helping to stimulate aggregate demand, which leads to economic growth in a country.
This policy is normally used by the government to get the economy out of recession or to promote economic growth, as shown in the diagram below.
The expansionary monetary policy tools that central banks use are:
By lowering interest rates, borrowing becomes inexpensive, which motivates individuals to borrow loans and spend more. Firms will also borrow more to invest.
Central banks can increase the money supply through quantitative easing, in which the government buys bonds or other financial assets to insert money into the economy. This increased money supply will increase aggregate demand and, hence, output and employment.
Expansionary monetary policy has the following main objectives:
The primary aim of using an expansionary monetary policy is to promote economic growth by increasing aggregate demand. This can be done to get an economy out of an economic downturn or to increase the growth rate of an economy by stimulating consumption, investment, and net exports, which are the main components of aggregate demand.
The second goal of an expansionary monetary policy is to reduce unemployment in an economy by encouraging businesses to invest and expand to create more jobs.
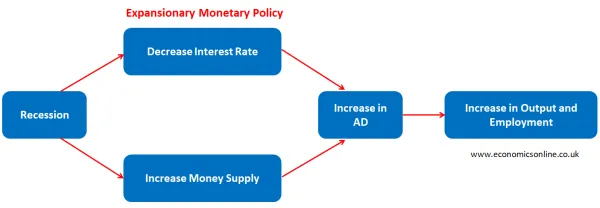
When a central bank decreases the discount rate and increases the money supply, it can increase aggregate demand by affecting its components like consumption (C), investment (I) and net exports (NX). This will work in the following ways:
Due to the lower interest rate, loans will become cheaper for individuals and firms and they will increase their consumption (C) and investment (I). The households will save less and spend more. Firms will also have an incentive to invest more as they are expecting higher consumption by households. This will increase the aggregate demand.
Due to a lower interest rate, exchange rate may also depreciate due to less demand of domestic currency by foreigners. This will make exports cheaper and imports expensive leading to an increase in the net exports, leading to an increase in the aggregate demand.
The central bank can increase money supply in many ways including the purchases of government bonds, open market operations, printing more money or encouraging commercial banks to increase lending by decreasing the reserve requirements.
Due to an increase in the money supply, individuals and firms will have more money which may lead to an increase in consumption and investment. As a result, the aggregate demand will increase.
The following graph illustrates the effect of an expansionary monetary policy.
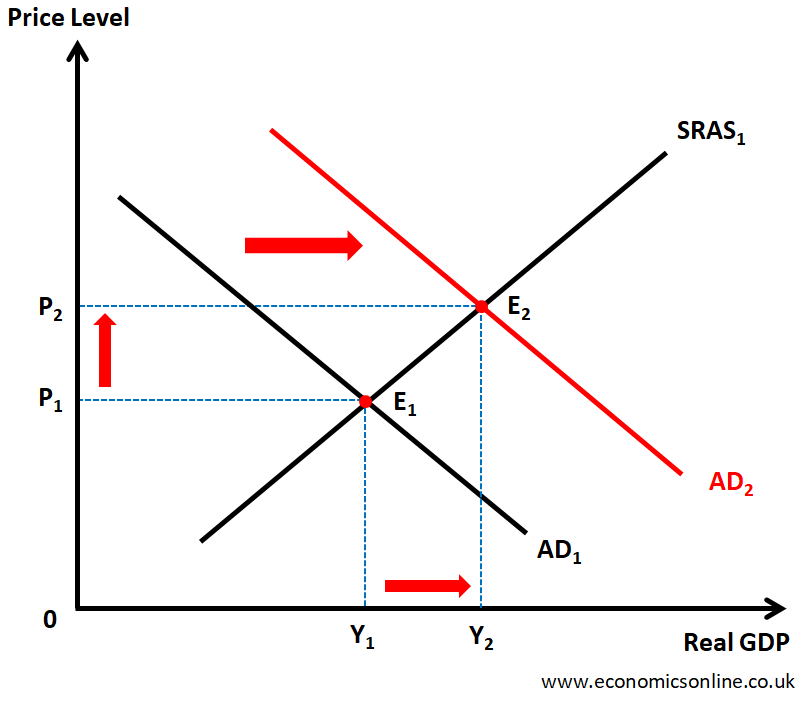
In the above graph, the Real GDP is taken on the horizontal axis (x-axis) while the price level is taken on the vertical axis (y-axis). The initial equilibrium is at E1 which is point of intersection of aggregate demand curve AD1 and short run aggregate supply curve SRAS1. The initial price level is P1 and the initial output level is Y1. When interest rate is decreased and money supply is increased, the aggregate demand curve is shifted towards right from AD1 to AD2. The new equilibrium point is E1. The real GDP is increased from Y1 to Y2 showing economic growth and a fall in unemployment. The general price level is increased from P1 to P2 showing a resulting inflation which is a side-effect of an expansionary monetary policy.
The above graph illustrates the impact of expansionary monetary policy on the following macroeconomic objectives of government.
Economic growth in a country will increase as a result of using an effective expansionary monetary policy. In the above graph, the real GDP is increased from Y1 to Y2 indicating economic growth.
The unemployment in a country will decrease as a result of using an effective expansionary monetary policy. In the above graph, the increase in real GDP from Y1 to Y2 indicates a fall in unemployment.
The inflation rate will increase as a result of using an expansionary monetary policy. In the above graph, the increase in price level from P1 to P2 indicates inflation. This is a negative effect of using an expansionary monetary policy. Central banks should keep check and balance on inflation and try to adjust their policies to maintain price stability.
There are several advantages of using an expansionary monetary policy, which are:
An expansionary monetary policy encourages borrowing, investment, and spending, which can stimulate overall economic activity and lead to higher GDP growth, by reducing interest rates and increasing the money supply.
An expansionary monetary policy encourages firms to borrow, invest and expand. This will create more jobs and hence unemployment level will fall.
Expansionary monetary policy strategies, such as quantitative easing, can help balance the financial markets during times of economic uncertainty. Injecting liquidity into the financial system can bring back confidence, prevent financial crises, and support a more stable market environment.
During periods of low inflation or deflation, expansionary monetary policy can help prevent a decline in prices by stimulating demand and encouraging spending. This can help maintain price stability and avoid prolonged periods of deflation.
Lower interest rates make borrowing more affordable for businesses and individuals, which can encourage investment in new projects, expansion, and consumer spending. This can have a positive impact on economic growth and business activity.
There are several disadvantages of expansionary monetary policy, which are:
By raising the money supply and reducing interest rates, expansionary monetary policy can lead to an increase in inflation. If the economy overheats and prices rise too quickly, it can reduce the purchasing power of people significantly.
Expansionary monetary policy can contribute to the establishment of asset price bubbles, such as in real estate or stock markets. When interest rates are low, investors may take on surplus risk, leading to inflated asset prices.
The long-term effects of expansionary monetary policy can lead to variance in the economy, such as excessive debt levels or over investment in certain sectors. These variances may create vulnerabilities that could contribute to future economic instability or financial crises.
Expansionary monetary policy measures, such as quantitative easing, can disproportionately benefit certain factors of society, such as asset owners or those with access to credit. This can worsen income inequality and widen the wealth gap.
Expansionary monetary policy may have limited effectiveness during economic recession when interest rates are already low. In such situations, other policy measures, such as fiscal stimulus or structural reforms, may be needed to support economic recovery.
During the economic recession of 2008 in the USA, the US economy was slowing down and the housing prices were falling. The Federal Reserve reduced interest rate and increased money supply by purchasing bonds and other securities to get the economy out of recession.
During the COVID-19 Pandemic, central banks around the world implemented expansionary monetary policy to combat the economic downturn.
Contractionary monetary policy aims to slow down the economic growth of a country and control inflation by decreasing borrowing and spending, increasing interest rates, decreasing money supply and by limiting access to credit.
Contractionary monetary policy is typically used when inflation becomes a concern and needs to be controlled.
The following table shows the comparison of the main features of expansionary monetary policy and contractionary monetary policy.
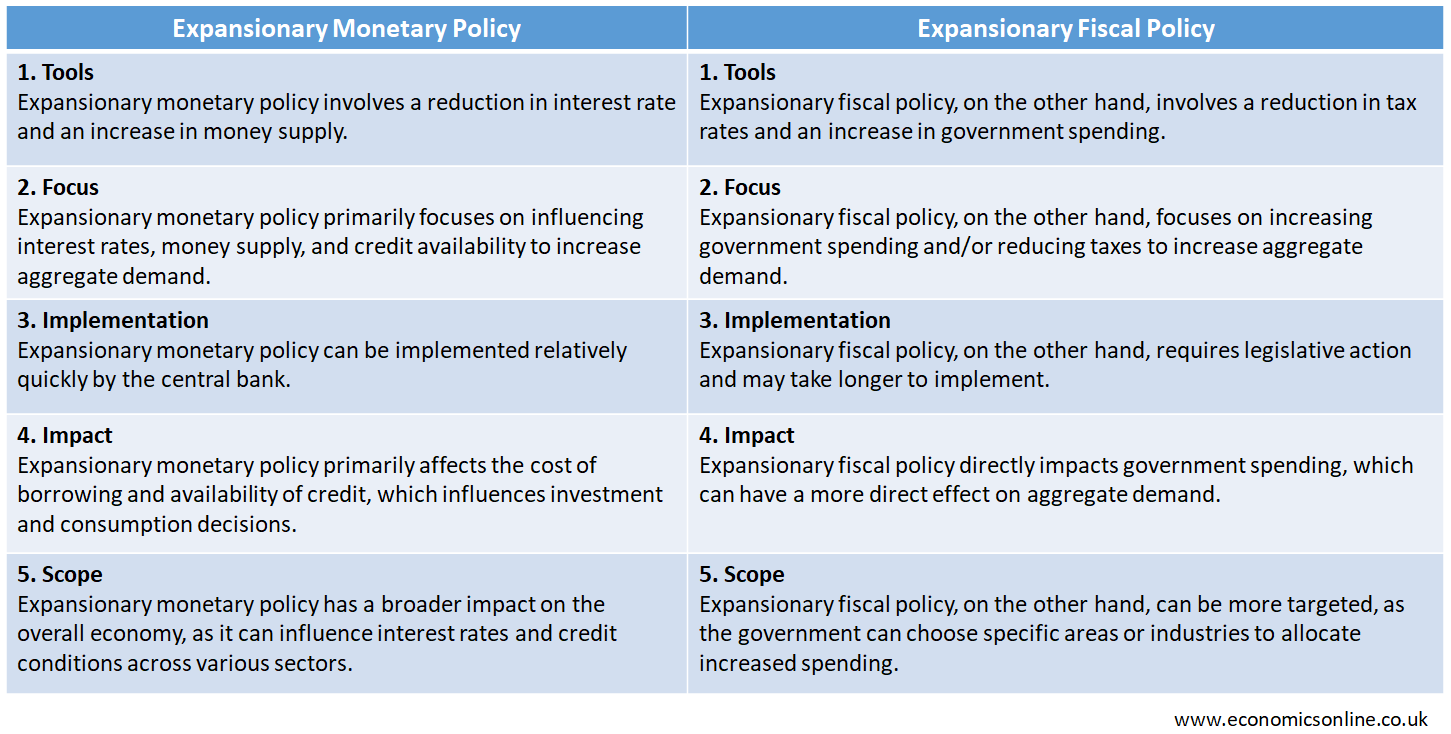
Expansionary fiscal policy refers to the policy of government to increase aggregate demand by reducing tax rates and increasing government spending. Both of these expansionary policies aim to increase aggregate demand but in different ways.
The following table compares the main features of expansionary monetary policy and expansionary fiscal policy.
In conclusion, expansionary monetary policy refers to the use of reduction in interest rate and an increase in money supply to increase aggregate demand in an economy. This policy can serve as a useful tool to achieve economic growth and tackle recession. However, this policy has some drawbacks such as inflationary pressure, asset price bubbles, unequal distribution of income, and the risk of future instability. Governments should keep a close check on inflation rates when using an expansionary monetray policy and take corrective measures if inflation becomes a matter of concern.